Evaluación del tiempo de inducción y la concentración de metanol en la expresión de L-asparaginasa II de Saccharomyces cerevisiae usando Pichia pastoris (Muts)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33017/RevECIPeru2015.0020/Keywords:
Pichia pastoris, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, L-asparaginase, MetanolAbstract
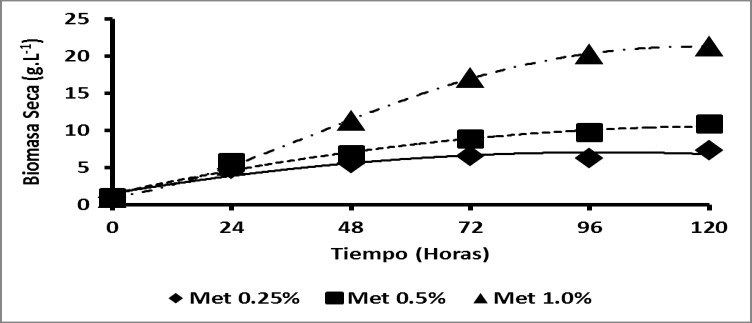
The methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris is widely used as a eukaryotic system for expressing recombinant proteins. Over 500 recombinant proteins were expressed in P. pastoris with expression levels reaching up to 80% of total secreted proteins and up to 30% total cell proteins. There are three phenotypes of P. pastoris classified according to their ability to metabolize methanol, phenotype MutS grows slowly on media containing methanol at generally low concentrations of methanol and longer induction time are used. Therefore, the control of culture conditions such as concentration of the inducer and the induction time are important factors for both yeast growth and for production of the protein since this system is controlled by the AOX promoter induced with methanol. Furthermore, L-asparaginase (EC. 3.5.1.1) is an important biopharmaceutical used to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), the enzyme commonly used in the therapy is from bacteria, these have shown good activity but cause many severe immune reactions in patients. The search for L-asparaginase derived and expressed in eukaryotic organisms opens a possibility to reduce adverse reactions. In this study they were evaluated the induction time (24-120 hours) and inducer concentration (0.25, 0.5 and 1.0% v/v). The data showed that the condition of increased expression of L-asparaginase II from Saccharomyces cerevisiae after 48 hours’ induction with 1.0% methanol (~ 25 U.g-1). Finally, it is recommended to evaluate this production in bioreactor where adequate control of other important variables such as pH of the culture and the concentration of oxygen in the medium is carried.