Estudio comparativo de la síntesis de nanopartículas de magnetita monodispersas
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33017/RevECIPeru2015.0001/Keywords:
Thermal decomposition, co-precipitation, ferrofluid, nanoparticles, transmission electron microscopyAbstract
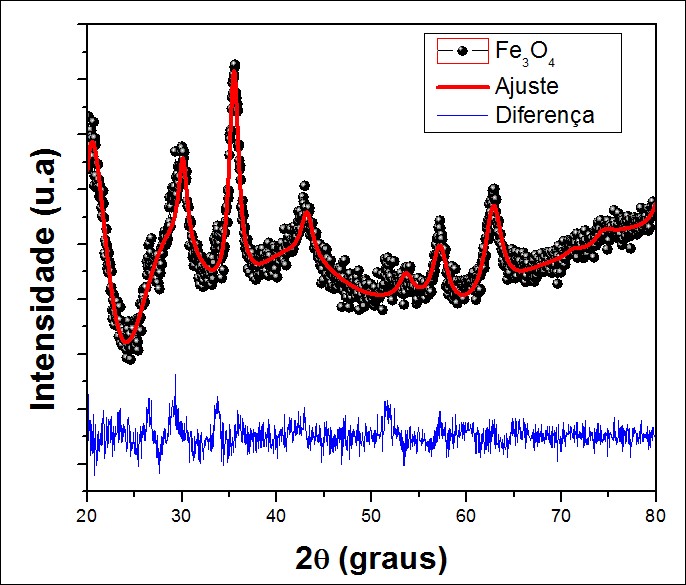
Currently the most studied type of magnetic nanoparticles are of cubic structure, inverse spinel, because these materials have very interesting features and possible applications since they facilitate building more complex systems. We must consider that due to the presence of transition metal on the surface of nanoparticles is that the conditions for funcionalizarlas with other molecules through complex functional groups obtaining materials with polar or apolar characteristics, depending on the type of implementation that want to use. Considering that when working with biological systems nanoparticles are detected by the reticuloendothelial system (RES). This functionalization is responsible for preventing agglomeration there of allowing them to remain in stable suspension (magnetic colloids) that can be driven by external magnetic fields. In this work, we show in detail the results obtained in improving the synthesis route system in the form of nanoparticles ferrofluid magnetite (Fe3O4) using the method of thermal decomposition and compare our results with respect to another synthesis route to nano particulate system method called chemical coprecipitation. To measure the size as well as knowing the morphological and structural properties of nanoparticles proceeded to the characterization of nanoparticles obtained by the methods of thermal decomposition and chemical co-precipitation through transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Size distribution averaging 8 nm and polydispersity of 0.14 was found. These results were corroborated by the results obtained by analyzing patterns of X-ray diffraction. The stability of the ferrofluid obtained was measured using the technique known as DLS (Dynamic Light Scattering), where it was found a value of 42.8 mV, which is within the expected value for a stable system, whereas for a nanoparticle system Zetasiser value above 30 mV represents a stability of the aqueous suspensión. At the end of characterization measures the extent of the value of the potential of hydrogen (pH) was performed using a pH meter, to study our sample having biocompatibility ferrofluid as our interest is that the ferrofluid could be used as vehicle for active ingredients or drugs addressing to a specific region in the body. And after completion of the measurement it was found a pH of 7.23 which shows a biocompatible system to possible biological applications.