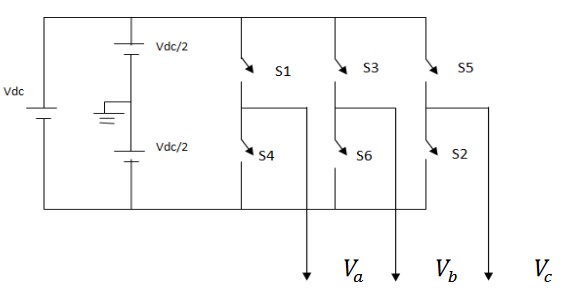
Caracterización del método SVPWM con inversor trifásico de dos niveles
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33017/RevECIPeru2019.0005/Keywords:
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation (SVPWM), Total Harmonic Distortion (THD), Voltage Source Inverter (VSI).Abstract
Alternating Current (AC) loads require variable voltage and variable frequency. These requirements are met by a voltage supply inverter (VSI). A variable output voltage can be achieved by varying the input DC voltage and keeping the inverter gain constant. On the other hand, if the DC input voltage is fixed and not controllable, a variable output voltage can be achieved by varying the gain of the inverter, which is normally achieved by controlling the pulse width modulation within the inverter. There are several pulse width modulation techniques, but the spatial vector technique is a good choice among all the techniques for controlling the voltage source inverter. Spatial vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM) is an advanced and very popular method with several advantages such as effective utilization of CC bus, less harmonic generation in output voltage, less switching losses, wide range of linear modulation, etc. In this document, a CC constant voltage source inverter has been taken and SVPWM has been implemented for two-level VSI using MATLAB / SIMULINK.