IMPORTANCIA DEL MICROAMBIENTE TUMORAL EN LA PROGRESIÓN DEL CÁNCER DE MAMA
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33017/RevECIPeru2008.0005/Keywords:
breast cancer, tumour microenvironment, metastasis, inflammation.Abstract
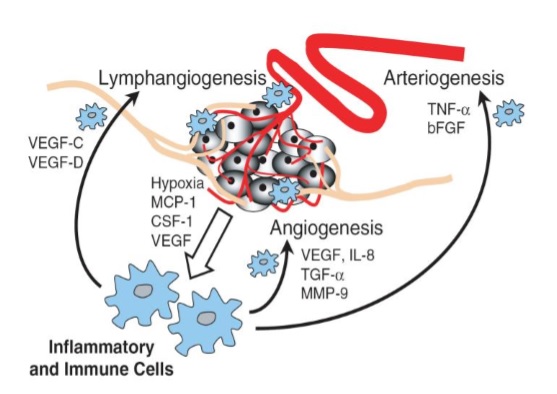
The epithelial tumour microenvironment is a complex tissue comprising variable numbers of tumour cells, fibroblasts, endothelial cells and infiltrating leucocytes. Cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, and proteases are key molecules controlling autocrine or paracrine communications within and between these individual cell types. Under some circumstances, endogenous cytokines may orchestrate host responses against the tumour, but there is increasing evidence that the cytokine network contributes to tumour growth, progression and host immuno-suppression. In addition, breast cancer progression is associated with and dependent upon robust neovascularization. It is becoming clear that tumour-associated „normal‟ cells, such as immune/inflammatory cells, endothelial cells and stromal cells, conspire with cancer cells in promoting this process. In this review we outline some of the actions of endogenous inflammatory cytokines and other molecules in tumor microenvironment over metastatic and invasive behavior of the breast carcinoma. A better understanding of these various cellular and molecular constituents of breast cancer microenvironment may be useful in designing more effective therapies.