EFECTO DE LA RADIACIÓN GAMMA SOBRE LAS CARACTERÍSTICAS MICROBIOLÓGICAS, FíSICO-QUÍMICAS y EVALUACIÓN SENSORIAL EN PIMIENTA NEGRA MOLIDA (Piper nigrum)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33017/RevECIPeru2010.0010/Keywords:
Gamma radiation, pepper, microbial population, dose.Abstract
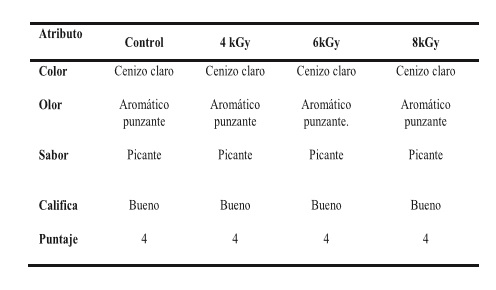
Pepper is the most famous of spices used to flavor foods. It is one of the crops with the highest microbial population, and it is causing disease and decay of mostly processed foods. The aim of this study was to determine the effect of gamma radiation on microbial population, the physicalchemical and sensory evaluation in ground black pepper, treated with different doses alternatives, in order to obtain the optimal minimal dose that reduces microbial load to the recommended specifications, without significantly altering the physical-chemical and sensory. 500 g samples were irradiated in the Gammacell 220 (0, 4, 6 and 8 kGy). The initial dose rate was 5.82 kGy/h. Were performed the following analysis: microbiological (aerobic mesophiles, anaerobes, Enterobacteriaceae, Salmonella / Shigella, total coliforms, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Lancefield group D streptococci, Bacillus cereus, Clostridium sulfite reducer, molds and yeasts). Physico-chemical (total ash, ash insoluble in HCl, HCl-soluble extract, alcohol, ether extract and crude fiber. Sensory evaluation (color, odor and flavor by descriptive test). The methods were those recommended by the FDA, APHA, AOAC and NTP. At different doses tested, there were no differences in physical-chemical analysis and sensory. The minimum dose of 8 kGy was selected that reduced the population of aerobic plate in 5 log units of 9,8 x 106 to 4.0 x 10 UFC/g, dose of 4 kGy was sufficient to reduce the fungal population by 3 log units of 1,7 x 103 to <10 UFC/g , according to the specifications.