FABRICACIóN y CARACTERIZACIóN DE SENSORES DE GAS NATURAL (GN) y GAS LICUADO DE PETRóLEO (GLP), BASADOS EN NANOPARTíCULAS DE ZNO
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33017/RevECIPeru2010.0004/Keywords:
Zinc oxide, colloid, nanoparticles, gamma radiation, gas sensor.Abstract
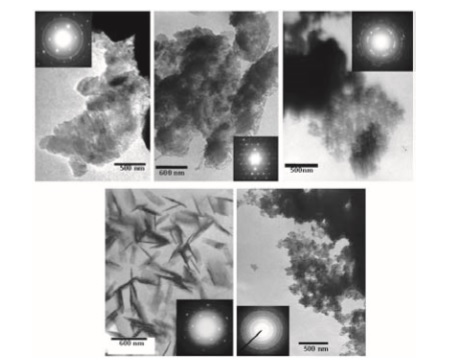
We have studied the influence of gamma radiation in a colloidal suspension of ZnO. A first ZnO colloid was prepared from Zn(CH3COO) 2.2H2O, LiOH.H2O and ethyl alcohol, while the second was prepared from Zn(CH3COO) 2.2H2O, NaHO and propyl alcohol. The ZnO colloids were irradiated at 30, 50, 75 and 100 kGy. These irradiated colloids were characterized by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and UV-Vis spectroscopy. ZnO films were produced by spray-pyrolysis technique from irradiated colloids, these films were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD). To evaluate the electrical properties of ZnO films, these films were fabricated on alumina substrates with gold electrodes printed and the system served us as gas sensor. The study of the dependence of the conductance with temperature in air, shows that the electrical conductivity of the sensors varies depending on the crystalline composition, operating temperature and the dose at which colloids have been irradiated. Different response patterns were found when the sensors are exposed to Natural Gas (NG) and Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG), typical responses of n-type, duals and p-type semiconductor sensors have been found.