PET recycling: Evaluation of the efficiency of contaminant separation PVC
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33017/RevECIPeru2011.0002/Keywords:
PET, PVC, plastic waste, recycling, separation, chemical treatment.Abstract
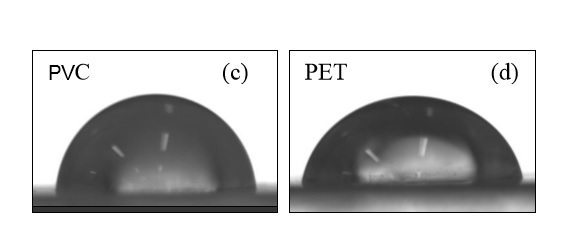
One of plastics conventional but used by the society is the PET (tereftalato polythene), widely used in the production of bottles for carbonated drinks and mineral water. Another plastic that also is used for that application, but in smaller amount is the PVC, (vinyl polychloride). The polymer recycling is important and advantageous, but it also exists disadvantages like the great volume of generated remainder, exhaustion of the sanitary fillings, among others. Diverse techniques of separation of polymeric materials exist, being the most used, the separation by difference of densidades (gravity), due to that is one of the methods but easy and cheap to be applied, the great problem of that method is the separation of materials with similar densidades, as it is the case of PET and PVC, between 1.30-1.37 g/cm3 disabling the separation of the same by that technique. The great problem is the contamination from PVC in the PET due to that it causes spots in the PET transparent as well its degradation. In this sense, the objective of that study is to determine the most efficient and economically viable methodology of separation from PVC in PET through flotation method. The first step was the treatment of the samples with alkaline solution of NaOH, 1.0 and 4.0% in mass, at temperatures of 25oC and 80oC, and times of treatment of 15 and 30 minutes. For the determination of the surface energy was realised the measures of contact angle using a goniometer. In the flotation test, solutions of MIBC of 0.25 and 0.5% were used and different pHs (acid, basic and neutral). Results of the conditions of thermo-chemical treatment showed that the solution with 1% of NaOH and 80 oC was the one that presented higher surface energies in the surface of the PET. In relation to the separation of the PVC by flotation, results showed that the condition more efficient was the basic, getting to reach a 85% of separation of PVC in solution of tensoactivo of 0.25% and 87% in solution of tensoactivo of 0.50%.