Sintesis del óxido de cobre nanoestructurado asistida con irradiación gamma o ultrasonido y sus propiedades antimicrobianas
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33017/RevECIPeru2011.0001/Keywords:
Nanoparticles, antimicrobial activity, sonochemistry, gamma radiation.Abstract
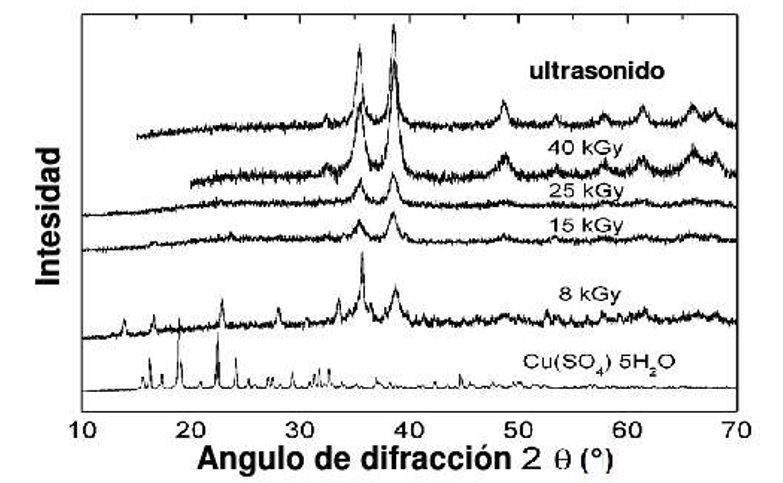
Copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles have been synthesized using gamma irradiation or ultrasound. The antimicrobial activity of CuO nanoparticles was determined by excavation method in plate culture in three microbial strains: Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923, Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853. The initial bacterial concentration was 1x107 CFU / mL and seeded onto Muller Hinton Agar and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. The CuO nanoparticles obtained by ultrasound are nanospheres with a higher antimicrobial activity for S. aureus than for E. coli and no activity against P. aeruginosa, while CuO nanoparticles obtained by gamma irradiation with a dose of 8 kGy have antimicrobial activity similar to S. aureus and E. coli and those obtained at doses of 15 and 25 kGy only have antimicrobial activity against E. coli.