Calidad nutricional de un producto extruido fortificado con dos niveles de hierro proveniente de harina de sangre bovina
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33017/RevECIPeru2013.0009/Keywords:
Bovine blood meal, extruded product fortified, nutritional quality, heme ironAbstract
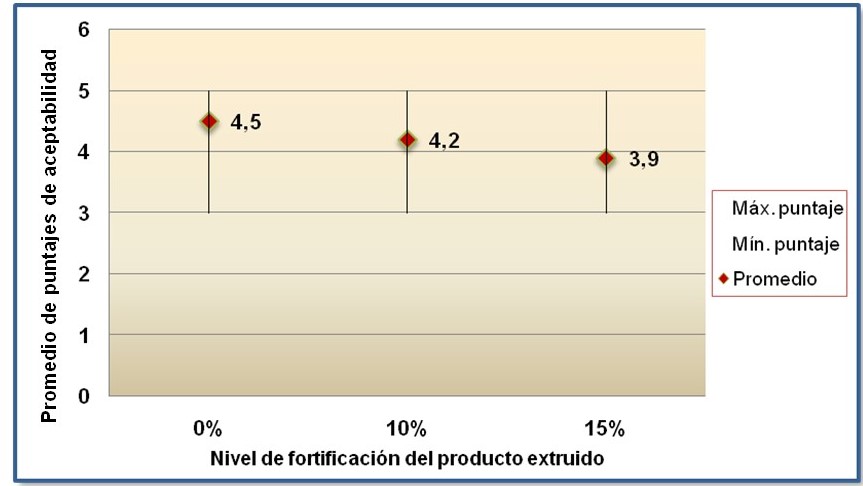
Iron deficiency anemia remains a major public health problem especially in developing countries where diets have low heme iron. Foods of animal origin such as bovine blood are a rich source of high iron content and most bioavailability by contain heme iron and its dehydration would be useful for fortification of extruded products. The objective of the research was to determine the nutritional quality of an extruded product fortified with two levels of iron from a bovine blood meal. A type of experimental technological study was realized. Bovine blood meal was obtained from a spray drying it was formulated with two levels of fortification of 10% and 15% also an unfortified product (0%) and for obtaining the extruded product was used a screw extruder auger at a temperature range between 158 °C to 162 °C in the Pilot Plant Food Industry Faculty of the Universidad Nacional Agraria La Molina (UNALM). The nutritional quality was determined from the iron content. Further proximate analysis, physical-chemical, microbiological was performed and acceptability test participated 60 students of Manuel González Prada N°2015 School, they were grouped into two panels: N°1: 5 to 6 years old and N°2: 13 to 15 years old. Respect to the result the extruded products fortified with 10% and 15% of iron from the bovine blood meal, had a high iron content 31,87 mg/100 g and 38,08 mg/100 g respectively as opposed to a lower iron content in the extrudate without fortify (0%) which was 2,99 mg/100 g. According to the proximate analysis was higher protein content extruded products fortified with 10% and 15% (12.47 g/100 g and 13.80 g/100 g, respectively) than 7.19 g/100g unfortified product. Through the physico-chemical analysis the rate of expansion was determined. It was median for unfortified extruded product (0%) and fortified with 10% and low expansion for product fortified with 15%. Microbiological analysis demonstrated that the extruded products were fit for human consumption. In the acceptability test to panel Nº1 was presented a 3-point hedonic scale and there was no significant difference between the three samples of extruded (p <0,05) and the panel Nº2 was presented a 5-point hedonic scale and there were significant differences between samples of extruded products with level of fortification of 0% and 15% (p<0,05). In conclusion, the extruded product fortified with 10% of iron from bovine blood meal showed an adequate nutritional quality and was more acceptable than the extruded product fortified with 15%. Consuming 40 g of this product would meet the recommendations of 12,6 mg of iron per day in children 4-6 years old and it could prevent iron-deficiency anemia.