L-Galactosa deshidrogenasa y L-Gulono-1,4-lactona deshidrogenasa influyen en la biosíntesis de vitamina C en Myrciaria dubia (Kunth) McVaugh “camu-camu”
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33017/RevECIPeru2012.0024/Keywords:
L-galactose dehydrogenase, L-gulone-1,4-lactone dehydrogenase, biosynthesis of vitamin C, Myrciaria dubia.Abstract
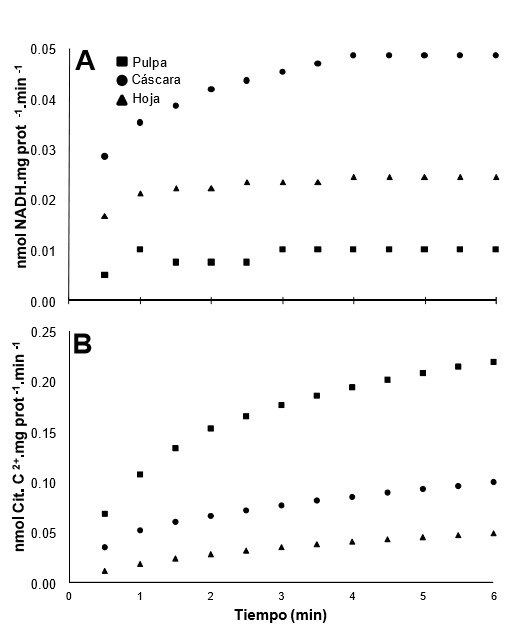
Vitamin C is an essential nutrient for humans and one their natural sources are fruits of Myrciaria dubia. But this plant shows wide variation in vitamin C. To help clarify the biochemical basis of this variation, we plan aims to determine whether the enzymes L-Galactose dehydrogenase (L-GalDH) and L-Gulone-1,4-Lactone dehydrogenase (L-GuLDH) are presents in leaves and fruits (pulp and peel) of camu-camu and compare catalytic activity of both enzymes in pulp of fruits harvested from plants that produce high and low content of vitamin C. Leaves and fruits were obtained from six plants (three producing low and three that produce high content of vitamin C) in the germplasm collection of INIA. Vitamin C was extracted and quantified by HPLC. Subsequently, from both groups of plants, was partially purified enzymes and measured by triplicate their catalytic activity by means of spectrophotometry. Both L-GalDH and L-GuLDH were detected in leaves, pulp and peel. Both enzymes showed differences in their catalytic activities among the tissues analyzed (p < 0.05). By comparing the activity of these enzymes between plants that produces fruits with high (2258±217 mg Vit. C/100g pulpa) and low (1570±46 mg Vit. C/100g pulpa) content of vitamin C significant differences were found (p <0.05) between groups. Being higher the catalytic activity of L-GalDH and L-GuLDH in fruits with high content in vitamin C and showed lower catalytic activity in fruits with low content in this vitamin. In addition, kinetic assays performed with the L-GuLDH of camu-camu showed that this enzyme has a high affinity (Km = 2.37 M y Vmax = 9.23 mol.mg prot-1 .min-1) for its substrate L-Gulone-1,4-lactone. In conclusion, the enzymes L-galactose dehydrogenase and L-gulone-1,4-lactone dehydrogenase are present in leaves and fruits of camu-camu, which indicates that the two biosynthetic pathways of vitamin C proposals for plants (pathway of Smirnoff-Wheeler and pathway of Wolucka) determine production of vitamin C in M. dubia. Furthermore, experimental evidences suggest that the accumulation of vitamin C in the pulp of the fruits of camu-camu depends at least of two processes: in situ biosynthesis and transport from other tissues with biosynthetic capacity. Furthermore, it is evident that catalytic activity of L-GalDH and L-GulDH influence in vitamin C content of pulp, so that a higher catalytic activity of both enzymes is associated with more vitamin C content in this tissue.