Aplicación subcutánea de dióxido de carbono para atenuación de cicatrices
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33017/RevECIPeru2012.0019/Keywords:
CO2, Carboxytherapy, Carbon dioxide Therapy, scars, skin regeneration.Abstract
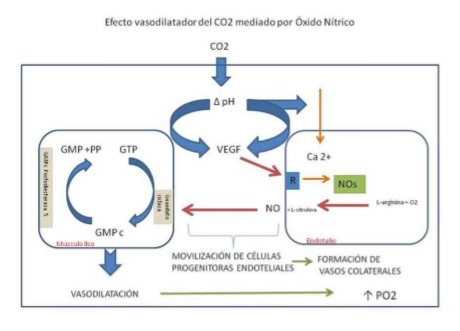
Carbon dioxide (CO2), is found in nature in a gaseous state. It is a colorless, odorless, and is a key part of the carbon cycle, its concentration in the air is 0.03%. CO2 is one of the basic components in the homeostasis of human body and is a result of cellular metabolism. CO2 is 20 times more soluble in water than in air and according to many scientific studies do not leading to no clinically significant embolism. In the blood circulation the carbon dioxide is transported to the lungs by three routes: 65% as bicarbonate ion, 25% as Co2 bound to proteins, especially the hemoglobin and plasma CO2 dissolved in 10%. [1]. In European countries like France and Germany, from the Middle Ages, are known the healing properties of carbon dioxide on circulation problems and skin, and since 1920 has been applied subcutaneous CO2 for medical treatment [2]. Current studies demonstrate the effect of carbon dioxide in blood microcirculation [3-6] and its effect on collagen increased after intradermal injection of the gas [7]. This healing process induced by CO2 is mediated by nitric oxide [8-10]. I present two cases of patients who came to the consulting room due stab wounds in the face both in superciliary region with a time of disease 10 days the first patient and 30 days the second. Both healthy men without contraindications for treatment and both wounds were sutured, showing fresh scar slightly depressed. Carbon dioxide was applied subcutaneously with a technique called Carboxytherapy, using Carboxiderm 1C equipment produced by Tonederm (Brazil) 30G/13 mm needles. The CO2 used was provided by Praxair, with a conformity certificate of 99.99% purity (certificate nº 12/000063). The subcutaneous and intradermal application was therefore in the wound area as a peripheral area thereof, to a maximum flow of 50 cc / min and a maximum of application volume of 300 cc. The application rate was 1 session every 1-4 weeks depending on the patient's progress. The results showed improvement in the skin, with attenuation of the initial scar, faster and better final result in the case of the most recent wound. The results agree with those found for Nach et al [11], in terms of improving skin appearance and decreased scarring. Whereas subcutaneous application of CO2, known as carboxytherapy, is safe and effective is a method that should be considered as a treatment of recent and old scars to stimulate a proper process of skin regeneration
and healing therefore, with a final result attenuation of residual scars.