Síntesis y caracterización de un compuesto semiconductor NiO-ZnO dopado con nanopartículas de Au por el método sol-gel para aplicación como sensores de gas
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33017/RevECIPeru2012.0002/Keywords:
NiO, ZnO, semiconductors, gas sensorAbstract
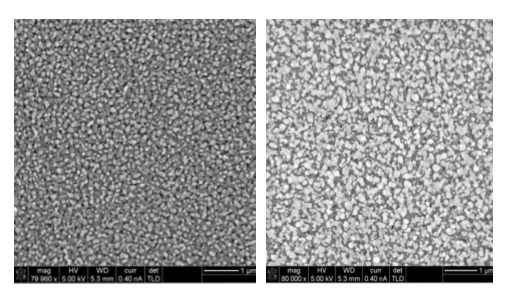
Porous films formed by a semiconductor ZnO-NiO (% mol) doped with Au nanoparticles (3% mol) were prepared by sol-gel method using nickel acetate tetrahydrate (NiC4H6O4.4H2O) and zinc acetate dihydrate (C4H6O4Zn.2H2O) as precursors, methanol (CH6OH) and ethanol (C2H6O) as solvents, monoethanolamine (C2H7NO) and diethanolamine (C4H11NO2) as functional chelants, and chloroauric acid (HAuCl4) as gold precursor. The samples were characterized by infrared (IR) and ultraviolet (UV-VIS) spectroscopy, microscopy SEM, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and gas sensing tests. The semiconductor samples were deposited on silicon substrates by spin-coating method at 2000 rpm, subsequently annealing at 500 and 600 °C. The effects of the compositions of NiO-ZnO and the percentage of doping are also discussed. The layer thickness was determined by ellipsometry in approximately 75 nm. These compounds were tested for gas sensors for H2 and CO (1% V/V) at 300 °C, showing excellent results for H2, but not for the CO.