ANÁLISIS BIOINFORMATICO DE LAS SECUENCIAS DE AMINOÁCIDOS DE DIVERSAS FOSFOLIPASAS D
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33017/RevECIPeru2004.0004/Keywords:
Phospholipase D, bioinformatics, biological databases, multiply alignment.Abstract
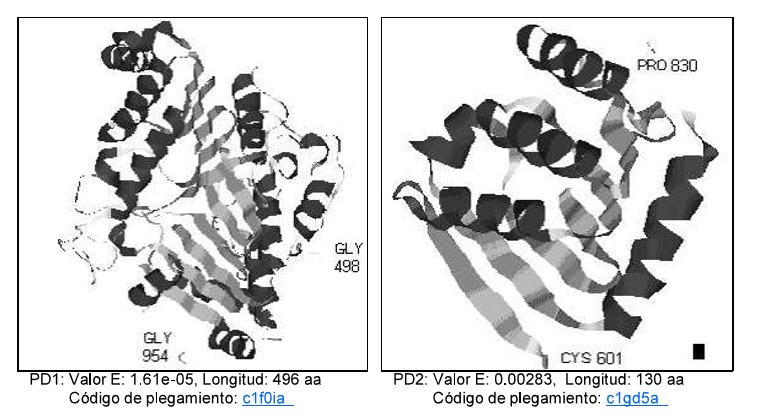
Phospholipases D are enzymes present in all eucariotic organisms, it was first discovered in plants and in recent years, increasing attention has been paid to its roles in signal transduction in mammals. Human isoforms of this enzyme D1 and D2 were analyzed using bioinformatic tools, predicting their chemical properties responsible of their different levels of action. Besides, using local multiply alignment programs like MACAW with amino acid sequences from different organisms, three conserved blocks of sequences in all organisms were detected. Between Plant sequences and not with bacterial, high similarity was detected. When these conserved blocks of sequence was visualized in determined experimentally 3D structure of Phospolipase D from Streptomyces Sp , an structural zone having near these blocks of sequence, was observed. This zone is postulated like an important structural feature of these enzymes that possibly contain essential amino acid residues for their biological activity.